You can specify filters in a query to restrict the data in the resulting dataset. A filter applies conditions on fields in a table that is associated with the query. For a field to be included in the resulting dataset, a field must meet the conditions of the filter.
Different Ways to Filter a Query Dataset
You can set up filters on a field from Query Designer or from C/AL code by using any of the methods that are outlined in the following table.
| Method | Filter | Description |
|---|---|---|
From Query Designer | Filter on a Data item | You can set the DataItemTableFilter property of a data item to filter on a field in the table of the data item. You can apply the filter to any field in the table, not just fields that are defined as columns in the resulting dataset. A data item filter cannot be overwritten from C/AL code. |
Filter on a Column | You can set the ColumnFilter property of a column to filter on the source field of the column. A filter on a column can be overwritten by the SETFILTER and SETRANGE functions from C/AL code. | |
Filter on a Filter row | A filter row lets you add a filter on a field that will not be included in the resulting dataset, but can be changed from C/AL code. To set up a filter row in Query Designer, you add a row of the type Filter that is set to the field thaaat you want to filter, and then set its ColumnFilter property.. A filter row is like a data item filter except a filter on a filter row can be overwritten by the SETFILTER and SETRANGE functions from C/AL code. | |
From C/AL | SETFILTER function | You can call the SETFILTER function from C/AL code to set a filter on a field that is exposed through a column or filter row. The filter that is set by the SETFILTER function will overwrite any filter that is applied to a column or filter row on the same field by the ColumnFilter property. |
SETRANGE function | You can SETRANGE function from C/AL code to set a filter on a field that is exposed through a column or filter row. The filter that is set by the SETRANGE function will overwrite any filter that is applied to column or filter row on the same field. |
Filtering From Query Designer
You can set up filters from Query Designer on data items, columns, and filter rows. You can set up multiple filters on the same field in addition to different fields.
Filtering with Data Items in Query Designer
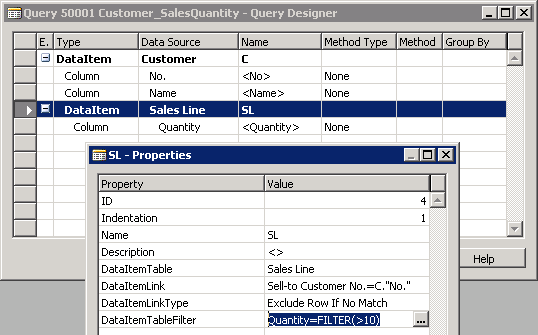
To specify filters on a data item in Query Designer, you set the DataItemTableFilter Property of a data item. You can apply a filter on any field in a table, not just those fields that are represented by a column in the query.
The following illustration shows Query Designer for a query that links table 18 Customer and table 37 Sales Line. The illustration includes the Properties window for the Sales Line data item that sets a filter to include only sales lines that have a quantity greater than 10.
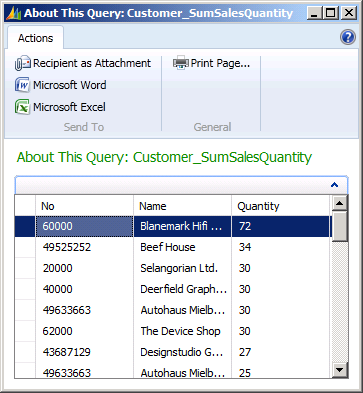
The following illustration shows the resulting dataset for the query.
A data item filter is static which means that it cannot be overwritten by a filter on a column or filter row in Query Designer or by the SETFILTER or SETRANGE functions in C/AL code. If one of these filter types is applied to the same field as the data item filter, then the filters are combined. In logical terms, this combination corresponds to an "AND" operation. For example, if the data item filter applies a filter on a field to include values greater than 10 (>10) and a column filter applies a filter on the same field to include values less than fifty (<50), then the resultant filter includes values that are greater than 10 and less than fifty (10< value <50).
The DataItemTableFilter property corresponds to a WHERE clause in an SQL SELECT statement. For more information, see Equivalent SQL SELECT Statements for Query Filters .
Filtering with Columns and Filter Rows From Query Designer
Unlike data item filters, filters on a column or filter row are dynamic and can be overwritten from C/AL code at runtime from a call to the SETFILTER or SETRANGE function that sets a filter on the same field.
You use filters on a column to filter on fields that are included in the dataset. To apply a filter on a column, you set the ColumnFilter Property of the column. You can apply a filter on any column, including aggregated columns that are applied a totals method by the Method Property.
You use filters on a filter row to filter on fields that you do not want included in the dataset. To set up a filter row, you add a row of the type Filter in Query Designer that specifies a field, and then set its ColumnFilter property. For more information about how to set up filter rows, see How to: Set Up Filter Rows in Query Designer.
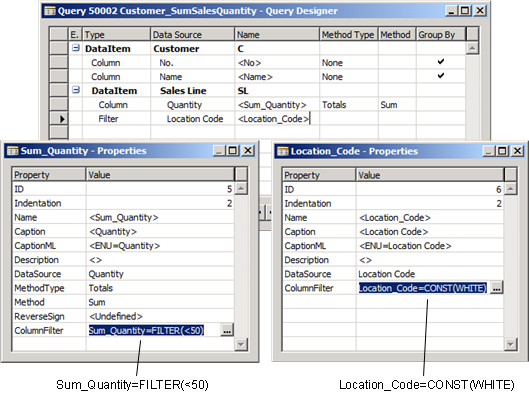
The following illustration shows Query Designer for a query that links the Customer table and the Sales Line table and retrieves the total quantity of items ordered for each customer. The query includes the following filters, as shown by the Properties windows in the illustration.
-
A filter on the Sum_Quantity column to include only records from the Sales Line table where the total quantity is less than 50.
-
A filter on filter row for the Location Code field of the Sales Line table that includes only records where the location code is WHITE.
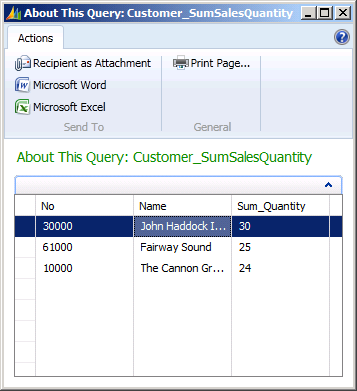
The following illustration shows the resulting dataset for the query.
In an SQL SELECT statement, filters on a column or filter row that do not apply a totals method, as with the Location Code filter row in the example, would correspond to a WHERE clause. Filters on a columns or filter rows that do apply a totals method, as with the Quantity column in the example, would correspond to a HAVING clause. For more information, see Equivalent SQL SELECT Statements for Query Filters .
Equivalent SQL SELECT Statements for Query Filters
If you are familiar with SQL, then it is helpful to know how filtering in Microsoft Dynamics NAV queries relates to SQL statements. To specify filters in an SQL statement, you use WHERE and HAVING clauses. The WHERE clause filters on fields. The HAVING clause filters on the results that have aggregated values as applied by of a totals method.
The following example shows the corresponding SQL SELECT statement for the previous data item filter example that links the Customer and Sales Line tables and filters on the Quantity field.
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
SELECT Customer."No.", Customer.Name, "Sales Line".Quantity FROM Customer LEFT OUTER JOIN "Sales Line" ON Customer."No." = "Sales Line".Sell-to Customer No. WHERE "Sales Line"."Quantity" > 10 | |
The following example shows the corresponding SQL SELECT statement for the previous column and filter row example that links the Customer and Sales Line tables and filters on the Location Code field and the total sum of the Quantity field.
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
SELECT Customer."No.", Customer.Name, SUM("Sales Line".Quantity) as Sum_Quantity
FROM Customer LEFT OUTER JOIN "Sales Line"
ON Customer."No." = "Sales Line".Sell-to Customer No.
WHERE “Sales Line”.”Location Code” = WHITE
GROUP BY Customer."No."
HAVING Sum_Quantity 50 | |
Filtering From C/AL Code
C/AL code includes the SETFILTER and SETRANGE functions that you can use to apply a filter on a field that is represented as a column or filter row in a query. The SETFILTER and SETRANGE functions enable you to set filters programmatically on a query at runtime. You use the SETRANGE function to filter on a range of values in a column or filter row. The SETFILTER function is more versatile than the SETRANGE function and enables you to filter a field based on a filter expression.
The SETFILTER and SETRANGE functions will overwrite any filter on the same field that is set on a column or filter row by the ColumnFilter property in Query Designer. If a SETFILTER or SETRANGE function filters on the same field as a filter on a data item, as specified by the DataItemTableFilter property, then the function filter and DataItemTableFilter property filter are combined.
Calling the SETFILTER and SETRANGE Functions
You can call the SETFILTER and SETRANGE function from the C/AL code of the Microsoft Dynamics NAV object that runs the query object or from the OnBeforeOpen Trigger of the query object.
To call the SETFILTER function, you use the following code.
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
Query.SETFILTER(Column, String) | |
Queryis a variable of the Query type that specifies the query object.Columnis the name of the column or filter row as defined by its Name property.Stringis the filter expression.
To call the SETRANGE function, you use the following code.
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
Query.SETRANGE(Column, FromValue, ToValue) | |
Queryis a variable of the Query type that specifies the query object.Columnis the name of the column or filter row as defined by its Name property.FromValueis the lower value of the range.ToValueis the higher value of the range.
For more information, see SETFILTER Function (Query) and SETRANGE Function (Query).
Example
Referring to the query example in the previous section, you can add the following code to the OnBeforeOpen trigger of the query object to change the filters on the Quantity column and the Location_Code filter row to include quantities of less than 50 and a location code of RED.
 Copy Code Copy Code | |
|---|---|
currQuery.SETFILTER(Sum_Quantity, '<50'); currQuery.SETFILTER(Location_Code, '=RED'); | |




