When you deploy Microsoft Dynamics NAV on Windows Azure or other cloud service for the first time, you will have a Microsoft Dynamics NAV environment that is configured for a single Microsoft Dynamics NAV company. The environment consists of a Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server instance, Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance, and Microsoft Dynamics NAV database. Depending on the network topology that you chose for deployment, the components will be deployed on one or two virtual machines.
After the initial deployment, you can begin to scale the topology by adding companies, Microsoft Dynamics NAV web server instances, Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instances, and Microsoft Dynamics NAV databases.
Scaling Configurations
There are three basic configurations for scaling up the Microsoft Dynamics NAV environment: single-instance, multiple-company, and multiple-instance.
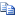
Single-Instance
With the single-instance configuration, each company has its own virtual machines that host the Microsoft Dynamics NAV web server instance, Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance, and Microsoft Dynamics NAV database. Companies or instances do not share resources.
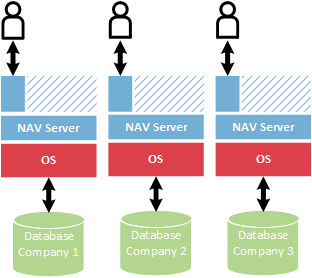
Multiple-Company
With the multi-company configuration, companies share the same Microsoft Dynamics NAV web server instance and Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance, and Microsoft Dynamics NAV database.
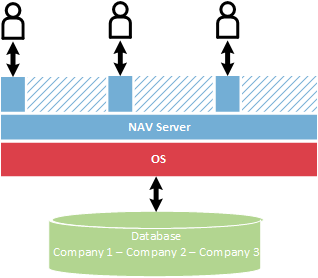
Multiple-Instance
With the multi-instance configuration, companies share the same Microsoft Dynamics NAV web server instance and Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance, but have their own Microsoft Dynamics NAV database.
Comparing the Configurations
The following table provides information that compares the different configurations to help you decide which configuration to use for your environment.
| Configuration | Single-Instance | Multiple-Company | Multiple-Instance |
|---|---|---|---|
Advantages | Full isolation on the operating system and database levels Each customer has their own virtual machine | Lowest resource consumption Easiest to upgrade and manage | Low resource consumption Easy upgrade of Microsoft Dynamics NAV Full isolation on the database level |
Disadvantages | No shared resources More expensive to set up and maintain | No database isolation No middle tier (Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server) isolation Single-point-of-failure for multiple customers | Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server consumes memory whether the customer is connected |
Recommended usage | When each virtual machine requires LOB software or configuration | When users read data only. In this case, no writing and process-isolation is required because data is shared between companies | When low resource consumption and full isolation are required, but you want to maintain process-level control of customers |
Memory used (approximate) | Operating system - 400 MB Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server - 200 MB User - 20 MB | Operating system - 400 MB Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server - 200 MB User - 20 MB | Operating system - 400 MB Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server - 200 MB User - 20 MB |
Shared memory | None | Operating system, Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server | Operating system |
How to Scale the Network Topology
To add the network topology, you use can use Microsoft Dynamics NAV Development Environment or Microsoft Dynamics NAV PowerShell cmdlets to add Microsoft Dynamics NAV web server instances, Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instances, Microsoft Dynamics NAV databases, and companies. For security, we recommend that you establish a remote desktop connection to the virtual machines.
See Also
Tasks
How to: Add a Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server InstanceHow to: Add a Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server Instance
How to: Add a Microsoft Dynamics NAV Database
How to: Add a Microsoft Dynamics NAV Company
How to: Change the Size of a Windows Azure Virtual Machine
Concepts
Network Topologies for Microsoft Dynamics NAV on AzureDeploying and Managing Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2013 on Windows Azure
Deploying Microsoft Dynamics NAV Using the Example Scripts